A Brief Look Into the URTeC SPE paper "Real-Time Hydraulic Fracture Optimization
Based on the Integration of Fracture Diagnostics and Reservoir Geomechanics"
By Pano Dalamarinis and Paul Mueller
Summary
On a five well project in the Eagle Ford, an operator used Seismos-FRAC™ to enable progressive treatment design changes during hydraulic fracturing operations. The goal of the project was to increase near-wellbore complexity, while stimulating the maximum reservoir volume without interfering with neighboring wells. Objectives were accomplished by using a real-time workflow that integrated fracture network complexity, conductivity and geometry measurements of the created fracture systems. These measurements coupled with rock property data along the lateral allowed for the optimization of treatment designs on a stage to stage basis.
Approach
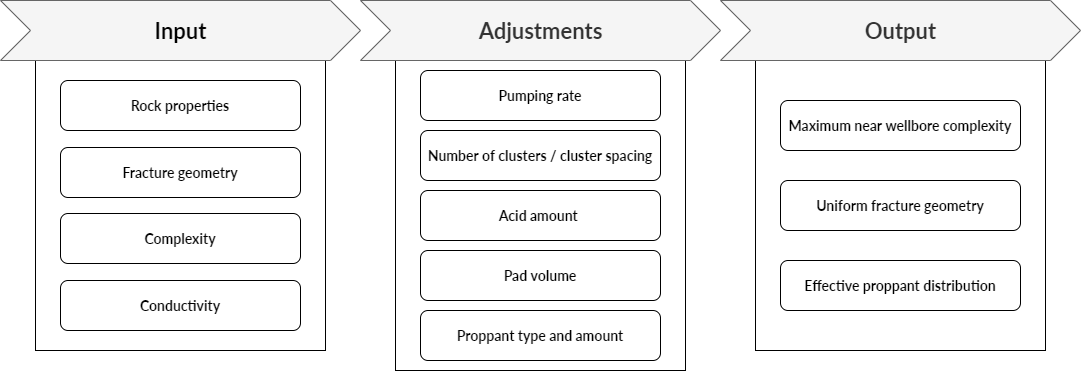
The first step of the workflow was to take a set of baseline measurements for the initial toe stages. Based on the measured fracture properties for those first stages, subsequent stage designs were adjusted to normalize the fracture half-length and further maximize near-wellbore complexity. These measurements, along with treatment parameters and rock properties, trained the machine learning interface (Seismos-AI™) to generate completion designs tailored for the various lithologies encountered along the lateral. Points of diminishing returns were identified for various completion parameters (fluid/proppant volumes, etc.) beyond which unjustified pumping time and expenses would accumulate without substantial benefit to stimulation. The workflow below represents the learning process of Seismos-AI™.
Results
Fracture networks with average half-lengths of 370 ft were created, while also maximizing near-wellbore complexity to improve overall production. With a well spacing of 660 ft, there was minimal to no unstimulated volume between the wells. By combining real-time fracture measurements along the lateral’s varying rock properties, Seismos-AI™ was successful in optimizing the stimulated reservoir to minimize inter-well communication and cut completion costs.
Full case study is to be presented at URTeC 2020. For more information to attend this presentation please visit Seismos.com/URTeC.